Industrial architect Hyun-Seok Kim, known for eccentric yacht designs, uses Voronoi diagrams as his latest inspiration:
Still at the design stage, the 125-meter vessel is adorned with a complex lattice exterior that its designer, South Korean industrial architect Hyun-Seok Kim, says is based on an algorithmic diagram by Georgy Voronoy, a math professor who lived under the Russian empire during the late 1800s.
I can’t wait for the subsequent bar, pie, and treemap yachts. They will be glorious.






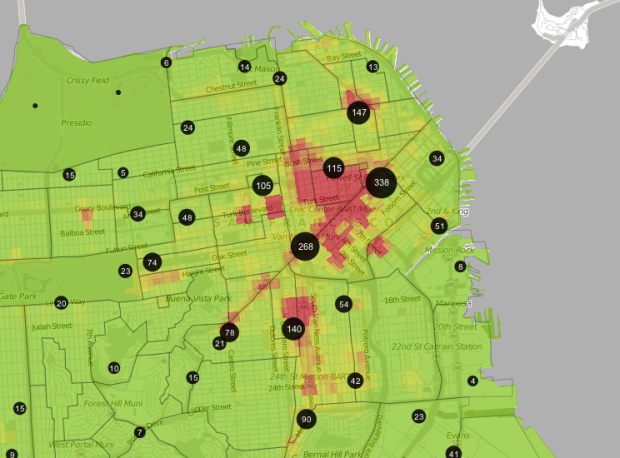
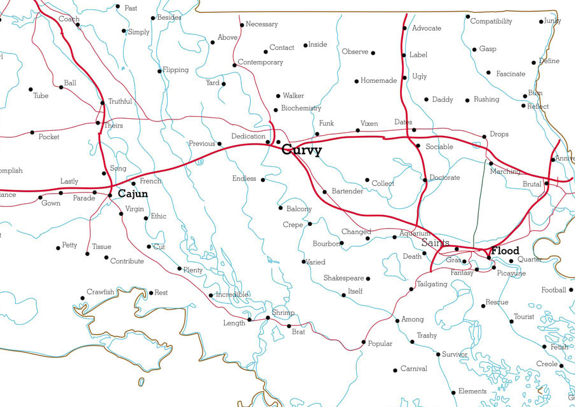
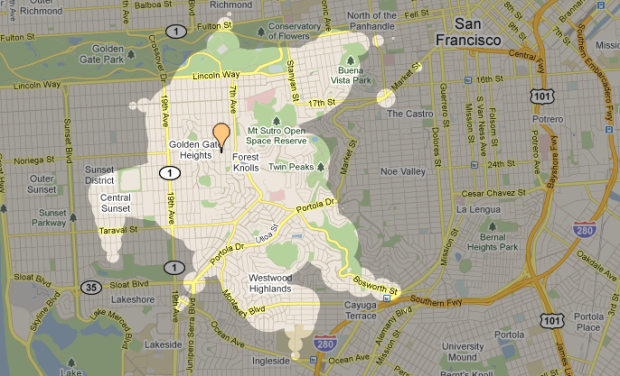

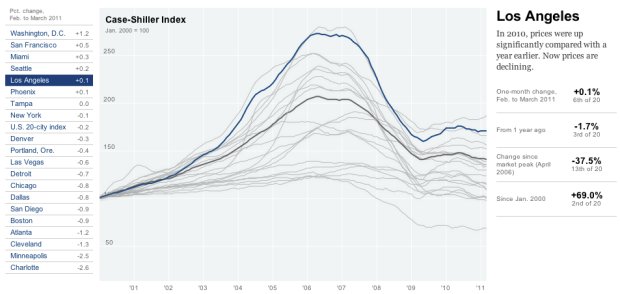

 Visualize This: The FlowingData Guide to Design, Visualization, and Statistics (2nd Edition)
Visualize This: The FlowingData Guide to Design, Visualization, and Statistics (2nd Edition)