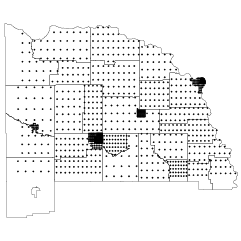
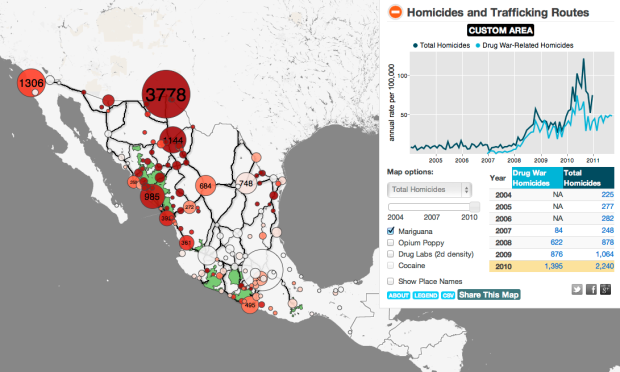
Diego Valle-Jones maps homicides and trafficking routes in Mexico.
To unclutter the map and following the lead of the paper Trafficking Networks and the Mexican Drug War by Melissa Dell, I decided to only show the optimal highways (according to my own data and Google Directions) to reach the US border ports from the municipalities with the highest drug plant eradication between 1994 and 2003 and the highest 2d density estimate of drug labs based on newspaper reports of seizures. The map is a work in progress and is still missing the cocaine routes, but hopefully I’ll be able to add them shortly.
There’s lots to look at and interact with here. To start, there are bubbles that cluster homicides by region and major highway routes in black.
Click on any bubble and you get a time series for the corresponding area, going back to 2004. Or if you like, draw your own polygon to see the time series for specific regions. Pointers on the time series highlight significant events. There’s also a slider that lets you see numbers on the map for different years. A layer underneath the bubbles lets you see high density areas for marijuana, opium, and drug labs.
Take a look at the full map for yourself. This is nice work by Valle-Jones.
[Diego Valle-Jones | Thanks, Diego]

 I thought this riveting post on the New York Times Bits blog about the
I thought this riveting post on the New York Times Bits blog about the 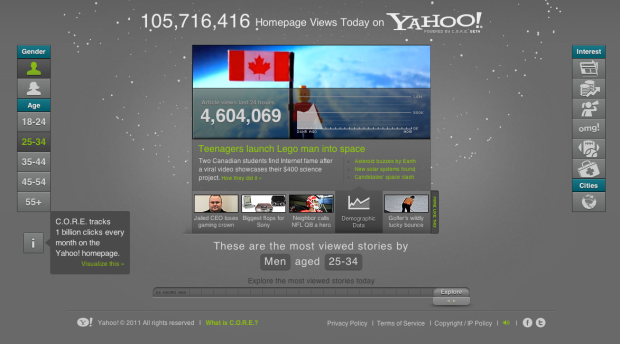

 Visualize This: The FlowingData Guide to Design, Visualization, and Statistics (2nd Edition)
Visualize This: The FlowingData Guide to Design, Visualization, and Statistics (2nd Edition)