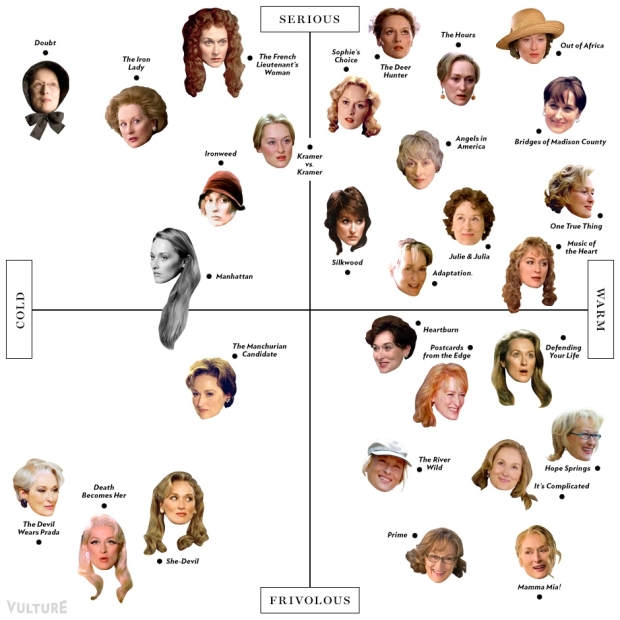
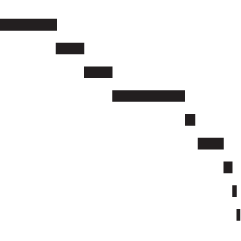Vulture plotted Meryl Streep’s character faces on a cold-warm, frivolous-serious scatterplot. Sure, why not.
-
-
-
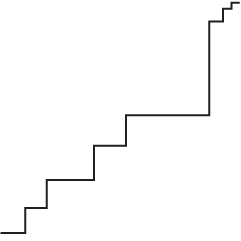
Brian Ball and M. E. J. Newman analyzed friendship data from a high school and junior high, and found a hierarchy similar to the one in Mean Girls.
Here we analyze a large collection of such networks representing friendships among students at US high and junior-high schools and show that the pattern of unreciprocated friendships is far from random. In every network, without exception, we find that there exists a ranking of participants, from low to high, such that almost all unreciprocated friendships consist of a lower-ranked individual claiming friendship with a higher-ranked one.
So someone higher up on the totem poll had more people saying they were friends with him or her, but the popular one didn’t necessarily feel the same.
I told my wife this, and her reaction was basically, “Uh, yeah. And?”
-
-
-
-
-
-
Expanding on his Vincent van Gogh pie charts, Arthur Buxton minimalized famous paintings from ten artists into more of everyone’s favorite chart type. The color distribution of each pie represents the five most used shades in each painting. Like the first time around, you’re either loving this or foaming at the mouth.
-
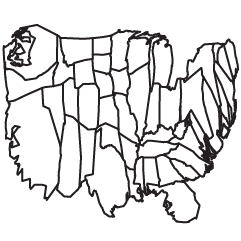
Renee DiResta got to wondering about state stereotypes, so she looked them up on Google and mapped them.
In the months before a US Presidential election, the quality of political discourse hits new lows. Blue State/Red State tropes dominate the news cycle as the media gins up outrage over perceived injustices in the culture wars. It’s all about our differences. So I started wondering, how do Americans really think about “those people” in other states? What are the most common stereotypes? For each of the fifty states and DC, I asked Google: “Why is [State] so ” and let it autocomplete. It seemed like an ideal question to get at popular assumptions, since “Why is [State] so X?” presupposes that X is true.
Roll over a state on the map, and the top four suggestions are listed. Hilarity ensues. “Why is California so… liberal, broke, anti-gun, and expensive?”
[via @rachelbinx]
-
-
Thousands of people have attended Edward Tufte’s one-day course on data graphics. Robert Kosara did not like it.
My advice? Buy his books. Read them. They’re good. Just realize that you’re getting a historical perspective on data visualization, not the cutting edge. Understand that Tufte’s ideas are a good starting point, not a religion. There are many things that Tufte doesn’t know, including pretty much anything related to visual perception and cognition, recent work (less than 30 years old), and interaction.
I’ve never been, but that’s sort of what I expected. Has anyone had a different experience with the course?
Update: Lots of good stuff in the comments. The consensus seems to be good/great for beginners, and others should stick to the books for refreshers.
-
-
-
-
Meters, by Berlin-based designers Patrick Kochlik and Monika Hoinkis, celebrates the joy of measuring for the sake of measuring. The pieces include a compass brooch and a bubble level that you wear as a watch, which is nice because everyone likes to know where they’re going while walking a level surface.
[via infosthetics]
-
In the what-happens-when-technology-takes-over-our-lives genre, Sight by Eran May-raz and Daniel Lazo, imagines a world where we wear contacts that augment our reality at such a high level that digital becomes physical. Life becomes a game, and everything is gamified, including an incredibly awkward date. But wait, there’s an app for that.
-
-




 Visualize This: The FlowingData Guide to Design, Visualization, and Statistics (2nd Edition)
Visualize This: The FlowingData Guide to Design, Visualization, and Statistics (2nd Edition)