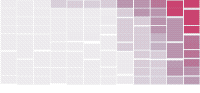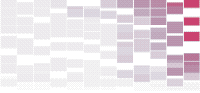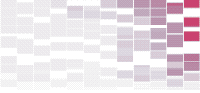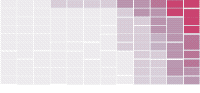
Shifting Causes of Death
Cause of death has changed over the years. In 1999, the suicide rate among 25- to 34-year-olds was 12.7 per 100,000 people. By 2016, that rate was almost 30 percent higher at 16.5.
These shifts over time are common and vary across sex and age groups.
With the release of the annual health report by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, I looked at the subcategories of mortality, as defined by the World Health Organization, focusing specifically on how the ten most common ways to die have changed over the years.
Each column represents an age group, and color represents rate within that age group. Mouse over any cause to highlight across all age groups.
As you might expect, mortality rate increases as you get older. The gradient from left to right makes this obvious.
If you keep an eye on specific causes, you spot some relevant rise and falls. For example, it is good to see HIV fall out of the top ten for middle-aged men and women after several years in the early 2000s as a most common cause.
However, the rise of intentional self-harm (i.e. suicide) in recent years, across the same age groups, is disconcerting. Suicide is high on the list for the full span of this dataset, but one would hope it would be on its way down.
How You Will Die
That’s how people die at various ages. Now here’s a simulation to see how this applies to you.
Notes
- I used R to analyze and prepare the data that I downloaded from the CDC’s WONDER database. That stands for Wide-ranging Online Data for Epidemiologic Research in case you were wondering. Government acronyms are just the best.
- I made the final graphic with D3.js.
- The CDC provides mortality data that goes back to 1968, but the classification of causes changed over the years, which makes it difficult to compare the full time span. Currently, the CDC splits it into three timespans: 1968-1978, 1979-1998, and 1999-2016.
Become a member. Support an independent site. Get extra visualization goodness.
See What You Get